Decentralized News: 20% Cost Reduction for U.S. Publishers by 2025
Decentralized news models are projected to reduce content distribution costs for U.S. publishers by 20% by 2025, offering a pathway to enhanced financial viability and fostering innovation in digital journalism.
The landscape of journalism is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving reader expectations. Among the most significant shifts is the emergence of decentralized news, a paradigm that promises to reshape how content is created, distributed, and consumed. This article explores the financial impact of decentralized news: estimating a 20% reduction in content distribution costs for U.S. publishers by 2025, a projection that holds immense implications for the future of media.
Understanding the Decentralized News Paradigm
Decentralized news represents a fundamental departure from traditional media structures, which are often centralized and reliant on intermediaries. This new model leverages technologies like blockchain to create a more direct, transparent, and efficient ecosystem for content. It aims to empower both creators and consumers by removing bottlenecks and reducing the influence of single points of control.
At its core, decentralization in news means distributing power and control across a network rather than concentrating it in a few hands. This can manifest in various ways, from how articles are published and verified to how revenue is shared. The shift promises not just technological innovation but also a recalibration of economic incentives within the news industry.
The mechanics of decentralized distribution
Decentralized distribution often involves peer-to-peer networks and blockchain technology. Instead of relying on a single server or platform, content is distributed across multiple nodes, making it more resilient to censorship and technical failures. This distributed ledger technology also provides an immutable record of content, enhancing transparency and trust.
- Blockchain-based platforms: These platforms record content creation and distribution, ensuring authenticity and provenance.
- Peer-to-peer networks: Content is shared directly between users, bypassing traditional hosting services and their associated costs.
- Tokenized incentives: Cryptocurrencies and tokens can reward content creators, curators, and even readers for their participation.
The appeal of decentralized news lies in its potential to address some of the most pressing challenges facing modern journalism, including declining revenues, trust deficits, and the rising costs of content delivery. By streamlining processes and cutting out intermediaries, decentralized models offer a compelling vision for a more sustainable and equitable media future.
In essence, understanding decentralized news is about recognizing its potential to democratize information flow and financial models in journalism. It’s a move towards greater autonomy for publishers and more direct engagement for audiences, all while aiming for significant cost efficiencies.
Current Challenges in Content Distribution Costs for U.S. Publishers
U.S. publishers today grapple with a complex array of expenses associated with content distribution. These costs significantly impact their bottom line, often hindering investment in quality journalism and innovation. Understanding these challenges is crucial to appreciating the potential relief offered by decentralized models.
Traditional distribution channels, particularly digital ones, involve a chain of intermediaries, each adding a layer of cost. From content delivery networks (CDNs) to platform fees and advertising technology, these expenses accumulate, making it difficult for many publishers to maintain profitability in an increasingly competitive market.
The burden of centralized platforms and ad tech
Many publishers rely heavily on major tech platforms for audience reach and monetization. While these platforms offer vast audiences, they also come with significant costs, including revenue sharing agreements and algorithmic dependencies that can impact visibility and traffic. The advertising technology stack itself is another major expenditure.
- Platform fees: Publishers often pay a percentage of their revenue or face strict terms for content distribution on social media and news aggregators.
- CDN expenses: High-volume traffic requires robust content delivery networks, which can be expensive, especially for global reach.
- Ad tech infrastructure: Maintaining and integrating various ad servers, exchanges, and data management platforms adds to operational overheads.
Beyond direct financial outlays, publishers also contend with indirect costs such as data management, cybersecurity, and the constant need to adapt to evolving technological standards. These factors collectively create a challenging environment where efficiency gains are constantly sought after. The current ecosystem, while effective in some respects, is undeniably expensive and often favors large tech conglomerates over individual news organizations.
The current distribution model forces publishers into a reactive stance, constantly optimizing for external platforms and investing heavily in infrastructure that doesn’t always yield proportional returns. This makes the prospect of reducing these entrenched costs not just appealing, but increasingly necessary for survival.
Mechanisms for Cost Reduction in Decentralized Systems
Decentralized news systems achieve cost reductions through several innovative mechanisms that bypass traditional intermediaries and leverage distributed ledger technology. These mechanisms address various aspects of content distribution, from hosting to monetization, offering a holistic approach to efficiency.
By shifting away from centralized servers and proprietary platforms, decentralized models inherently reduce infrastructure overheads. They distribute the burden of storage and bandwidth across a network of participants, often incentivized by token economics, rather than relying on a single, expensive provider.
Direct-to-consumer distribution and reduced platform fees
One of the most significant cost-saving avenues is the ability to distribute content directly to consumers, minimizing or eliminating the need for third-party platforms that charge substantial fees. This direct connection fosters greater financial autonomy for publishers.
- Elimination of middlemen: Content can be published and accessed without going through expensive aggregators or social media platforms.
- Lower hosting costs: Distributed storage solutions, often blockchain-based, can be significantly cheaper than traditional cloud hosting services.
- Efficient micro-payments: Native cryptocurrency payment systems allow for frictionless micro-transactions, unlocking new revenue streams without high transaction fees.
Furthermore, the transparency and immutability of blockchain can reduce costs associated with ad fraud and content verification. By providing an auditable trail of content and engagement, decentralized systems can restore trust in advertising metrics, leading to more efficient ad spending and potentially higher returns for publishers.
The inherent security features of decentralized networks also contribute to cost savings by reducing the need for extensive cybersecurity measures typically required for centralized systems. This robust and distributed infrastructure makes it harder for malicious actors to disrupt content delivery or compromise data, thereby preventing costly breaches and downtime.

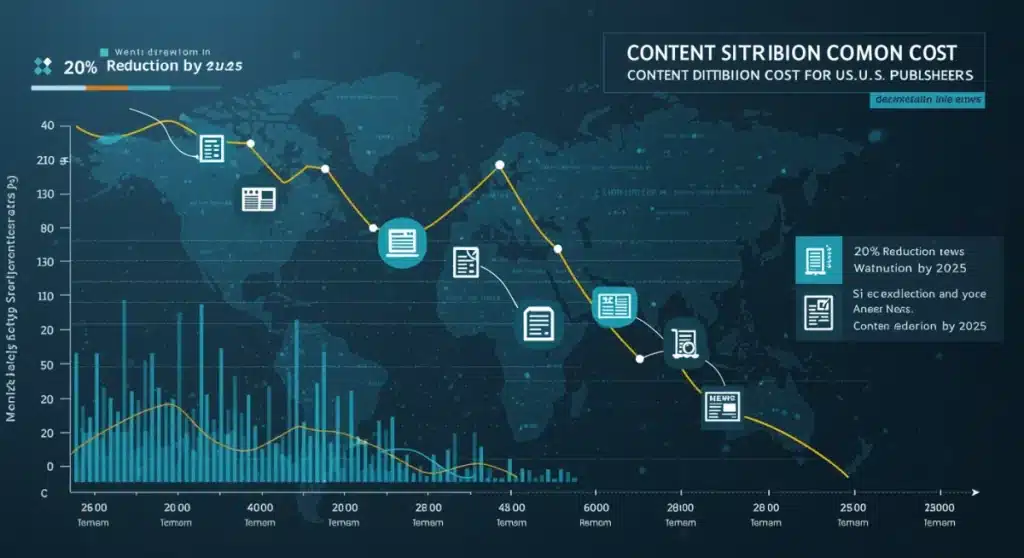
Projected 20% Reduction: A Detailed Analysis for U.S. Publishers
The estimation of a 20% reduction in content distribution costs for U.S. publishers by 2025 is not an arbitrary figure; it’s a projection based on the tangible efficiencies decentralized news systems offer. This reduction is expected to materialize through a combination of technological advancements and widespread adoption.
Breaking down this 20% figure involves examining various cost centers within traditional publishing and identifying where decentralized models can make the most significant impact. These include infrastructure, platform fees, advertising technology, and fraud prevention measures, all of which represent substantial outlays for publishers.
Key areas contributing to the 20% saving
The savings are anticipated to come from several fronts, each contributing a portion to the overall reduction. The cumulative effect of these efficiencies is what drives the optimistic projection.
- Infrastructure savings (5-7%): Reduced reliance on expensive CDNs and centralized servers through distributed hosting.
- Platform fee avoidance (7-10%): Bypassing large tech platforms that demand a significant share of revenue or impose high distribution costs.
- Ad tech optimization and fraud reduction (3-5%): More transparent and verifiable advertising pipelines, minimizing losses from ad fraud and inefficient ad spend.
- Operational efficiencies (1-3%): Streamlined content verification, rights management, and payment processing through blockchain.
This 20% reduction is a conservative estimate, acknowledging the time required for widespread adoption and the initial investment in transitioning to decentralized systems. However, as the technology matures and becomes more accessible, the potential for even greater savings in the long term becomes increasingly plausible. Early adopters are already seeing promising results, validating the underlying principles of these cost-saving mechanisms.
The cumulative effect of these individual savings creates a powerful argument for the adoption of decentralized news models. It represents a significant financial reprieve for an industry often struggling with profitability, allowing resources to be redirected towards journalistic endeavors rather than overheads.
Case Studies and Early Adopters in the Decentralized News Space
While the concept of decentralized news is still evolving, several projects and publishers are already demonstrating its potential, providing valuable insights into its practical application and financial benefits. These early adopters serve as proof points for the projected cost reductions and operational efficiencies.
From independent journalists leveraging blockchain platforms for direct audience engagement to established media houses experimenting with tokenized content, the landscape of decentralized news is rich with innovation. Their experiences offer a glimpse into the future financial models of journalism.
Pioneering projects and their impact
Various platforms and initiatives are leading the charge, each with a unique approach to decentralization. Their successes, even on a small scale, highlight the viability of these new models.
- Civil (now defunct but influential): Although Civil faced challenges, its vision for blockchain-based journalism inspired many, demonstrating the potential for transparent content creation and ownership.
- Steemit/Hive: These platforms reward content creators and curators with cryptocurrency, offering a direct monetization model that bypasses traditional advertising.
- Basic Attention Token (BAT) and Brave Browser: This ecosystem allows users to tip creators directly with BAT, creating a new revenue stream and reducing reliance on traditional ad networks.
These examples, among others, illustrate how decentralized technologies can foster more direct relationships between content creators and consumers, leading to reduced reliance on costly intermediaries. Publishers experimenting with these models report not only cost savings but also increased audience engagement and a stronger sense of community around their content. The lessons learned from these early ventures are critical for refining future decentralized news architectures.
The experiences of these early adopters, despite occasional hurdles, provide a robust foundation for the broader adoption of decentralized news. They underscore the practical benefits, particularly in cost efficiency, and offer a blueprint for other publishers looking to navigate this new frontier in media.
Roadblocks and the Path to Widespread Adoption
Despite the compelling financial benefits and innovative potential, the path to widespread adoption of decentralized news is not without its challenges. Technical hurdles, user education, and regulatory uncertainties all present significant roadblocks that need to be addressed.
Transitioning from established, centralized systems to a decentralized architecture requires substantial investment in new technologies, training, and a shift in organizational mindset. These are not trivial undertakings, especially for organizations with limited resources or entrenched operational practices.
Overcoming technical and user experience challenges
The underlying blockchain and Web3 technologies, while powerful, can be complex for the average user and publisher. Simplifying these interfaces and ensuring seamless integration are crucial for broader acceptance.
- User interface complexity: Many decentralized applications (dApps) currently have steep learning curves, deterring mainstream users.
- Scalability issues: Some blockchain networks struggle with transaction speeds and volumes, which can be problematic for high-frequency news dissemination.
- Interoperability: Ensuring that different decentralized news platforms and tools can communicate and integrate effectively is vital for a cohesive ecosystem.
Beyond technical considerations, there’s also the challenge of educating both publishers and consumers about the benefits and mechanics of decentralized news. Building trust in new financial and content models takes time and consistent effort. Regulatory frameworks around cryptocurrencies and blockchain are still evolving, adding another layer of uncertainty for publishers considering a full transition.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative effort from technology developers, media organizations, and policymakers. By focusing on user-friendly interfaces, scalable solutions, and clear regulatory guidelines, the industry can pave the way for a smoother and more rapid transition to decentralized news, ultimately realizing its full financial and journalistic potential.
The Future Landscape: Beyond 2025 and Long-Term Impact
Looking beyond the immediate projection of a 20% cost reduction by 2025, the long-term impact of decentralized news promises an even more transformative shift for U.S. publishers and the media industry as a whole. This future landscape envisions a more robust, resilient, and equitable ecosystem for journalism.
The initial cost savings are just the beginning. As decentralized technologies mature and become more integrated into journalistic workflows, they are expected to unlock new revenue models, enhance editorial independence, and foster greater public trust in news sources. The implications extend far beyond mere financial efficiency.
Evolving revenue models and journalistic independence
Decentralized platforms can facilitate direct reader support through subscriptions, donations, and micro-payments, reducing reliance on volatile advertising markets. This financial independence can empower publishers to prioritize quality journalism over clickbait.
- Subscription tokens: Unique tokens can grant access to premium content, creating a transparent and direct subscription model.
- Creator economies: Journalists can directly monetize their work through NFTs, personal tokens, or direct tipping, fostering independent reporting.
- Community governance: Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) could allow communities to fund and govern news initiatives, ensuring alignment with public interest.
Furthermore, the immutable nature of blockchain can help combat misinformation by providing verifiable content provenance, rebuilding trust in an era of widespread digital skepticism. This enhanced credibility, coupled with more efficient distribution, could lead to a resurgence in public engagement with quality news. The long-term vision is one where journalism is not only financially sustainable but also more accountable and responsive to its audience’s needs.
The long-term impact of decentralized news is not merely about cutting costs; it’s about fundamentally reimagining the economic and ethical foundations of modern journalism. It presents an opportunity to build a media landscape that is more resilient, transparent, and ultimately, more valuable to society.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Reduction Target | 20% reduction in content distribution costs for U.S. publishers by 2025. |
| Key Mechanisms | Direct-to-consumer distribution, reduced platform fees, optimized ad tech via blockchain. |
| Financial Impact | Enhanced sustainability, reallocated resources for quality journalism, new revenue streams. |
| Challenges Ahead | Technical complexity, user education, regulatory uncertainties for widespread adoption. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Decentralized News Costs
Primary cost savings stem from reduced reliance on centralized content delivery networks (CDNs), elimination of high platform fees charged by major tech companies, and more efficient, transparent advertising processes that minimize fraud. These factors collectively contribute to a leaner operational model for news distribution.
A 20% reduction in content distribution costs will significantly enhance the financial sustainability of U.S. publishers. It will free up capital that can be reinvested into investigative journalism, technological innovation, and talent acquisition, ultimately leading to higher quality content and a more competitive media landscape.
Blockchain technology minimizes costs by enabling peer-to-peer content distribution, removing the need for expensive intermediaries. It also provides transparent and immutable records for content verification and ad impressions, reducing fraud and streamlining payment processes with lower transaction fees through cryptocurrencies.
Yes, adopting decentralized news models typically requires initial investments in new software infrastructure, employee training on blockchain and Web3 technologies, and potential redesigns of content management systems. However, these upfront costs are expected to be offset by long-term operational savings and new revenue opportunities.
Key challenges include the current complexity of decentralized technologies for mainstream users, scalability issues in some blockchain networks, and the need for greater interoperability between platforms. Additionally, regulatory uncertainties and the effort required for widespread adoption and user education pose significant hurdles.
Conclusion
The projected financial impact of decentralized news: estimating a 20% reduction in content distribution costs for U.S. publishers by 2025, represents a pivotal moment for the media industry. This shift is not merely about technological novelty but about fundamentally restructuring the economic foundations of journalism. By leveraging blockchain and peer-to-peer networks, publishers can significantly cut overheads, reclaim financial autonomy, and redirect resources towards producing high-quality, trustworthy content. While challenges in adoption and education remain, the long-term benefits of a more efficient, transparent, and resilient news ecosystem are undeniable, promising a healthier future for journalism in the digital age.